The Javanese language features a complex system of honorifics that vary according to the social status of the speaker, listener, and referent. Despite its cultural and linguistic significance, there has been limited progress in developing a comprehensive corpus to capture these variations for natural language processing (NLP) tasks. In this paper, we present Unggah-Ungguh, a carefully curated dataset designed to encapsulate the nuances of Unggah-Ungguh Basa, the Javanese speech etiquette framework that dictates the choice of words and phrases based on social hierarchy and context. Using Unggah-Ungguh, we assess the ability of language models (LMs) to process various levels of Javanese honorifics through classification and machine translation tasks. To further evaluate cross-lingual LMs, we conduct machine translation experiments between Javanese (at specific honorific levels) and Indonesian. Additionally, we explore whether LMs can generate contextually appropriate Javanese honorifics in conversation tasks, where the honorific usage should align with the social role and contextual cues. Our findings indicate that current LMs struggle with most honorific levels, exhibiting a bias toward certain honorific tiers.
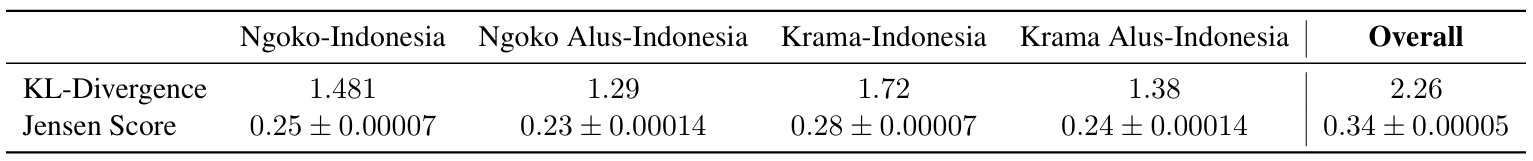
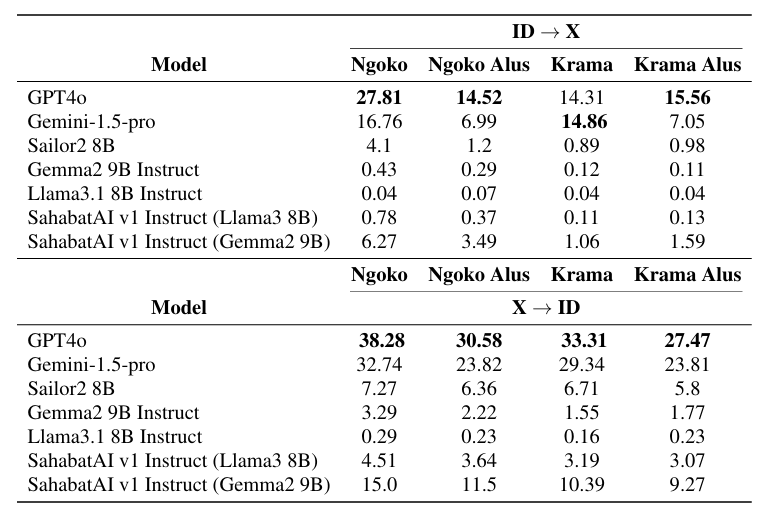
Current research indicates that existing models struggle to accurately interpret and generate Javanese honorifics due to the absence of a well-annotated corpus,, which in turn hinders the development of effective NLP tools capable of handling their complexity. Moreover, as illustrated in Figure 2, most existing Javanese corpora exhibit an imbalanced distribution of honorific levels, further limitating model performance.
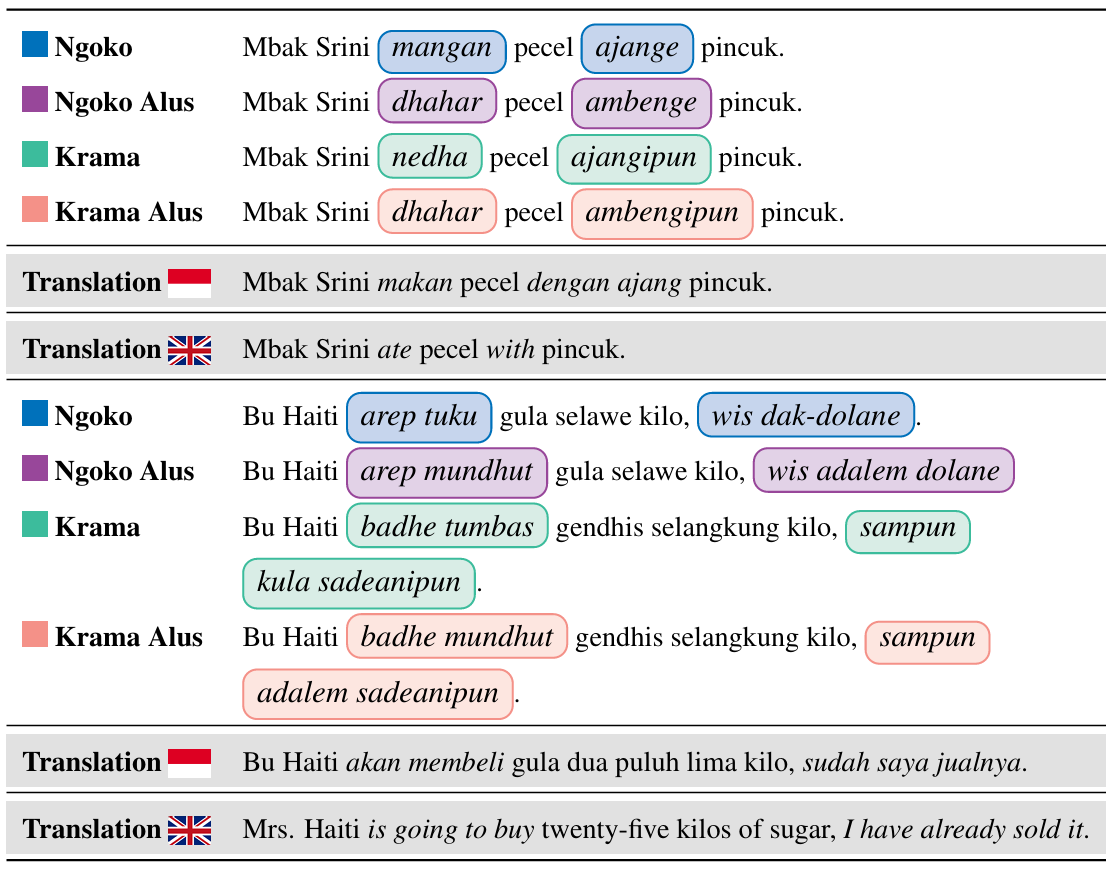
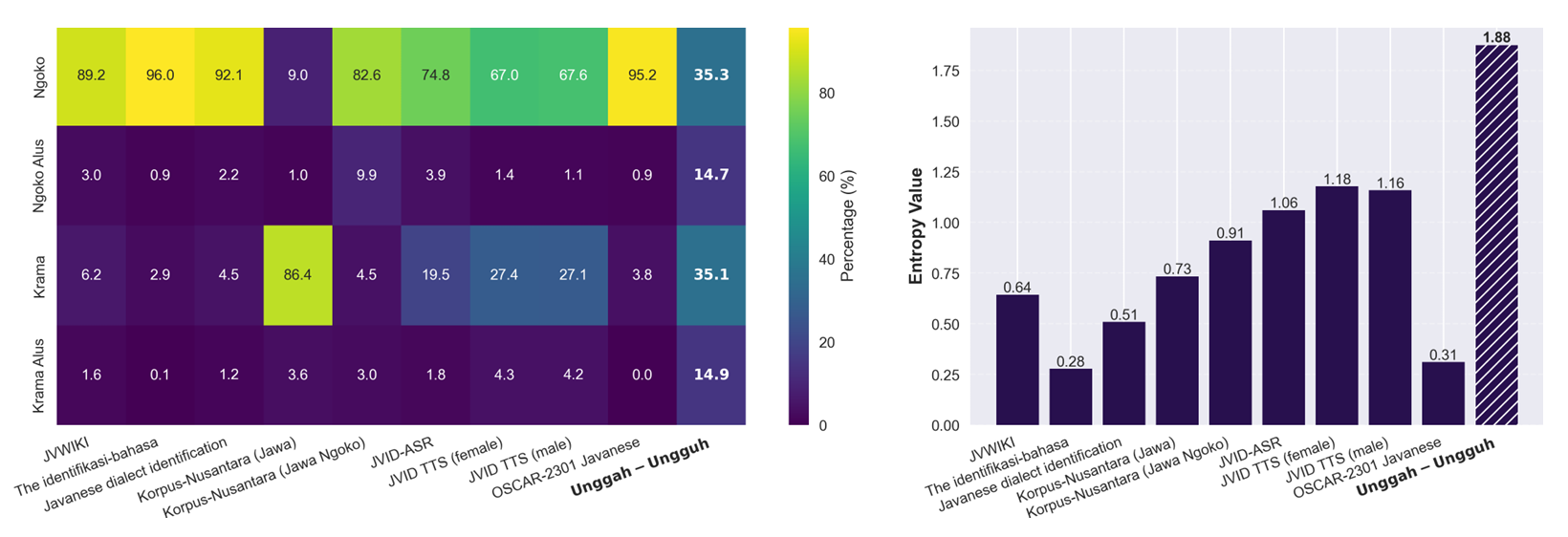

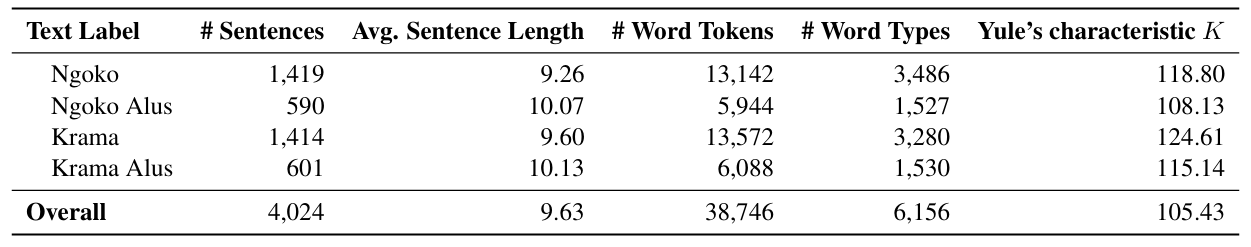
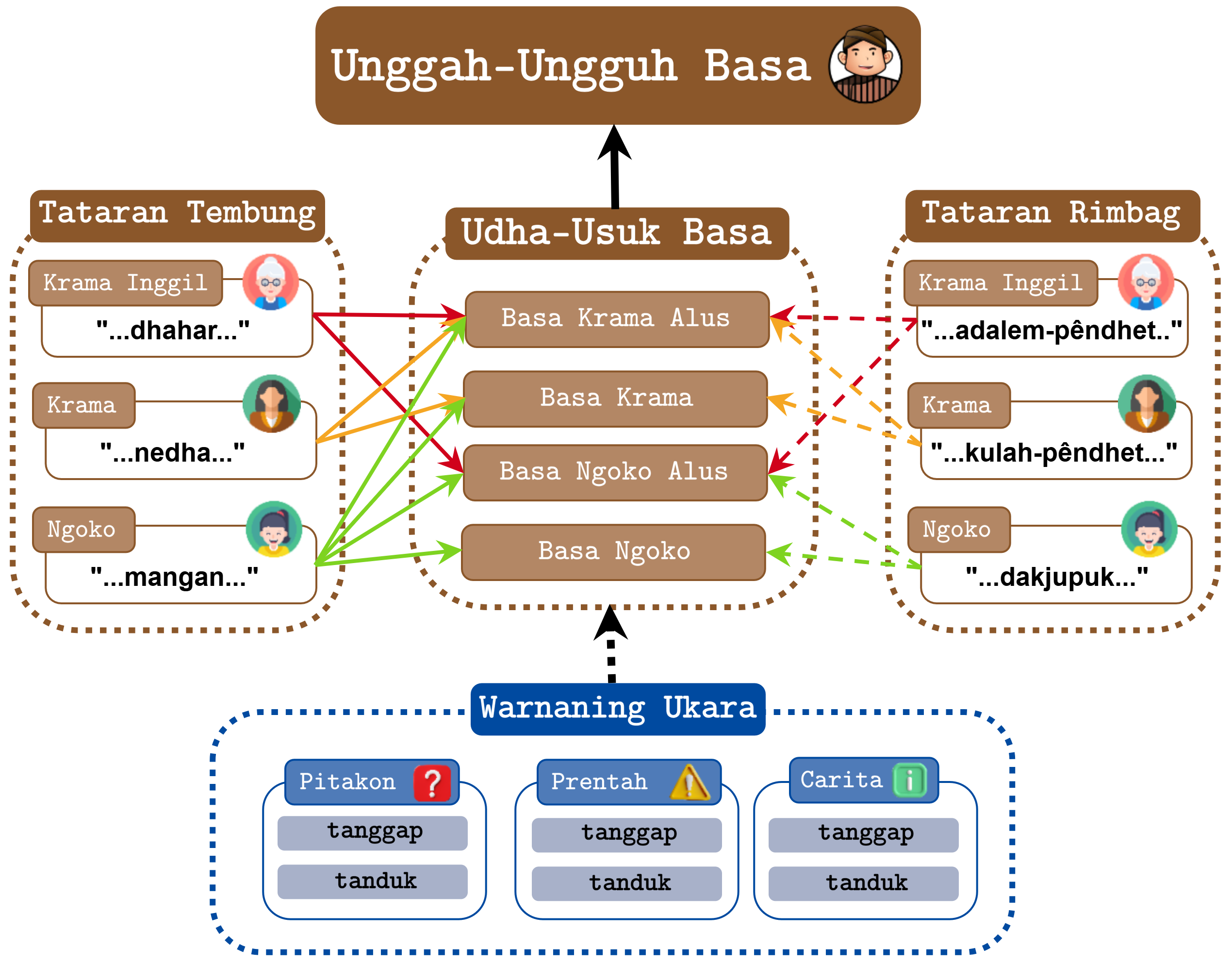
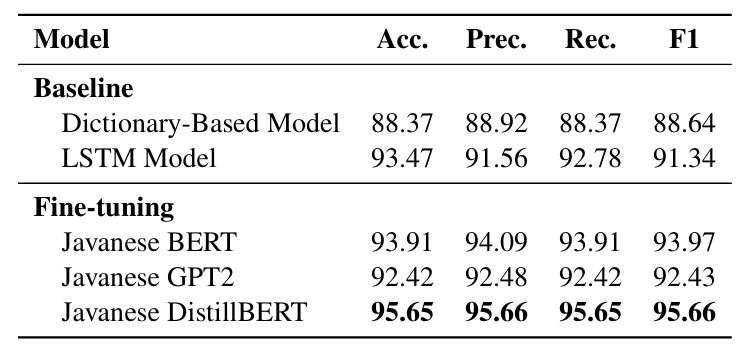
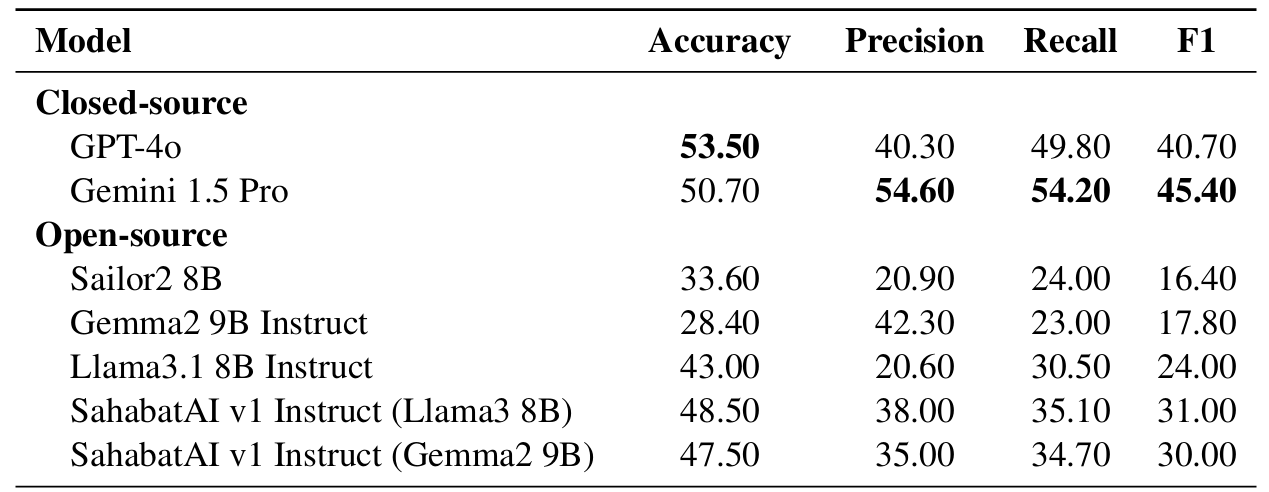
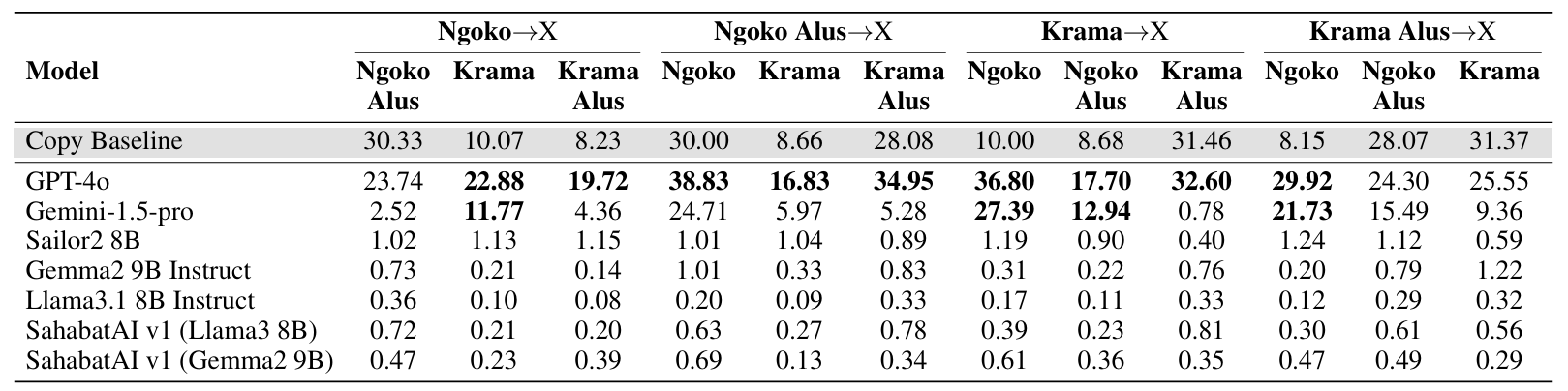
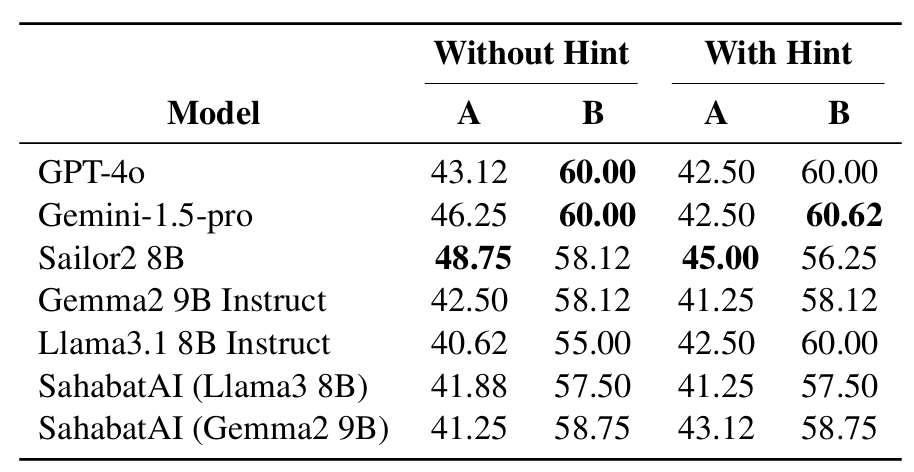
In our benchmark, we want to train and evaluate LMs' understanding to various language styles in different honorific levels. Our benchmark comprises four downstream NLP tasks; Honorific Level Classification, Honorific Style Change, Cross-lingual Honorific Translation, and Conversation Generation with Honorific Persona. Our experimental results reveal that LLMs exhibit a bias toward a specific honorific level, primarily due to imbalanced distribution of honorific tiers in existing Javanese datasets. This study's methodologies and datasets provide a foundation for future research on low-resource languages with complex honorific systems.
@article{farhansyah2025language,
title={Do Language Models Understand Honorific Systems in Javanese?},
author={Farhansyah, Mohammad Rifqi and Darmawan, Iwan and Kusumawardhana, Adryan and Winata, Genta Indra and Aji, Alham Fikri and Wijaya, Derry Tanti},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.20864},
year={2025}
}